Orthopedics
Orthopedics and Joint Replacements?
Orthopedics is a medical field that focuses on the examination, treatment, and prevention of conditions and injuries affecting the human locomotors system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and nerves. Orthopedic surgeons are the medical professionals who specialize in this field and are trained to provide comprehensive care for musculoskeletal disorders.
Joint replacement is a common orthopedic process that involves replacing a injured or diseased joint with an unnatural joint, also known as a prosthesis. The most common replacements are hip, knee and shoulders. but it can also be performed on the joints such as elbow or ankle.
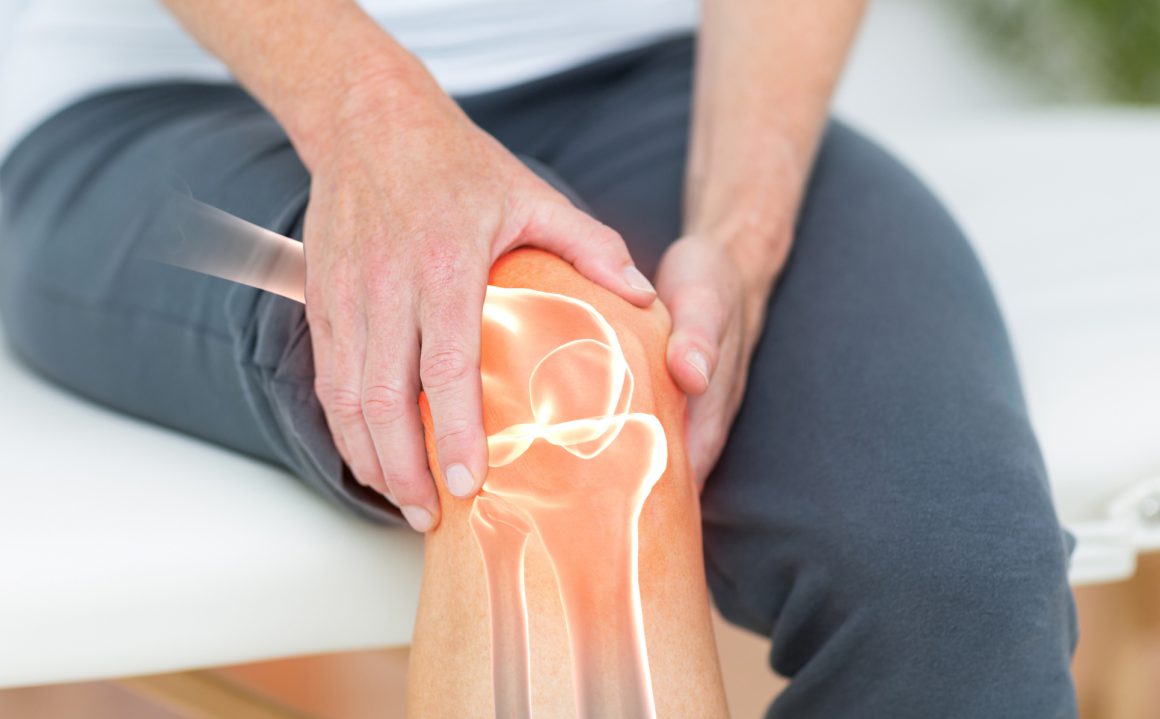
Our Speciality
Orthopedics We Offer :
1) Complete and partial knee replacement
2) Complete and partial shoulder replacement
3) Hip replacement
4) Ankle replacement
5) Elbow replacement
Steps of joint replacements in our Hospital
The joint replacement process typically involves several key steps, from initial evaluation and preparation to surgery, recovery, and rehabilitation. Here is an overview of the joint replacement process:
Initial Evaluation: The process begins with an assessment by an orthopedic surgeon. The surgeon will go through your medical history, direct a physical examination, and order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the extent of joint damage. Based on the evaluation, the surgeon will determine if joint replacement is an appropriate treatment option for you.
Preoperative Preparation: If joint replacement is recommended, you will undergo preoperative preparation. This may involve additional medical evaluations, such as blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), or consultations with other specialists to ensure you are medically fit for surgery. The surgeon will also discuss the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and answer any questions or concerns you may have.
Surgical Procedure: The orthopedic surgeon will perform the joint replacement surgery using the chosen surgical technique. They will make an incision to access the affected joint, remove damaged or diseased joint surfaces, and replace them with artificial joint components (prostheses). The prostheses are secured in place using screws, cement, or other fixation methods. The length of the surgery depends on the joint being replaced and the complexity of the procedure.
Recovery and Hospital Stay: After te surgery , you will be shifted to monitor area , where you will be monitored like when you wake up from anesthesia , about all your recoveries and stuff. once you are stable you will be moved to a hospital room where you will be taken care of .
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation and physical therapy are crucial components of the joint replacement process. Soon after surgery, a physical therapist will work with you to start gentle exercises and mobility training. Gradually, you will progress to more challenging exercises to regain joint function, strength, and mobility. The duration and intensity of rehabilitation will depend on the joint replaced and your individual progress.
Postoperative Care and Follow-up: After leaving the hospital, you will continue to receive postoperative care and have follow-up appointments with your orthopedic surgeon. These appointments allow the surgeon to monitor your progress, remove any stitches or staples, and address any concerns or
complications that may arise. You will receive guidance on wound care, pain management, medications, weight-bearing restrictions, and a gradual return to activities.
Orthopedicians, also known as orthopedic surgeons or orthopedic doctors, are medical professionals who specialize in the field of orthopedics. They are physicians who have undergone extensive training in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions and injuries affecting the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Diagnosis: Orthopedicians utilize their expertise and knowledge to assess patients and diagnose various musculoskeletal conditions and injuries. They conduct thorough medical history reviews, physical examinations, and may order diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, CT scans, or blood tests to help identify the source of the problem.
Treatment Planning: Once a diagnosis is made, orthopedicians develop treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs. They consider factors such as the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and goals. Treatment options may include non-surgical interventions such as medication, physical therapy, exercises, assistive devices, or lifestyle modifications. In some cases, orthopedicians may recommend surgical intervention.
Surgical Interventions: Orthopedic surgeons are trained to perform a wide range of surgical procedures to address musculoskeletal conditions and injuries. These surgeries can include joint replacement, fracture fixation, arthroscopy (minimally invasive procedures using a camera and specialized instruments), ligament repair, tendon reconstruction, spinal surgery, and more. They use their surgical skills and knowledge to correct deformities, repair injuries, and restore function and mobility.
Trauma Care: Orthopedicians play a critical role in the management of orthopedic trauma, such as fractures, dislocations, and other acute injuries. They assess and stabilize fractures or injuries, often in collaboration with other medical specialists, such as emergency medicine physicians, trauma surgeons, anesthesiologists, and rehabilitation specialists. They may perform surgical procedures to realign and fix fractures or treat complex injuries.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation: After surgery, orthopedicians provide postoperative care and guidance to ensure proper healing and recovery. They work closely with physical therapists and rehabilitation specialists to develop individualized rehabilitation programs for patients. These programs aim to restore joint function, strength, and mobility through exercises, therapies, and gradual return to activities.
Chronic Conditions and Degenerative Diseases: Orthopedicians also manage chronic conditions and degenerative diseases that affect the musculoskeletal system. These can include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, and other conditions. They offer various treatment options to alleviate pain, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life. Orthopedicians specialized in specific areas within orthopedics, such as sports medicine, joint replacement, pediatric orthopedics,
